Vitamins and Minerals
What is a vitamin?
Vitamins are a large number of micronutrients other than proteins, fats and carbohydrates that are found in food. Vitamins are very powerful nutrients and all cells need vitamins. Without vitamins, metabolism slows down and people age more quickly.
What are the functions of vitamins?
Vitamins are essential for metabolic reactions. They do not contain calories and do not cause weight gain. Most of them are not synthesized in the body and must be taken from outside with food. Provides energy from carbohydrates, fats and proteins. They help biochemical regulation in cells and are used in the construction of tissues and organs, in the maintenance of intact nutrients and in reducing the effects of certain harmful substances.
Uses of vitamins
Vitamins are used for physical performance enhancement (beauty-aesthetics), mental performance enhancement (anti-aging), disease prevention (antioxidants) and disease treatment (replacement).
What are the vitamins we must take?
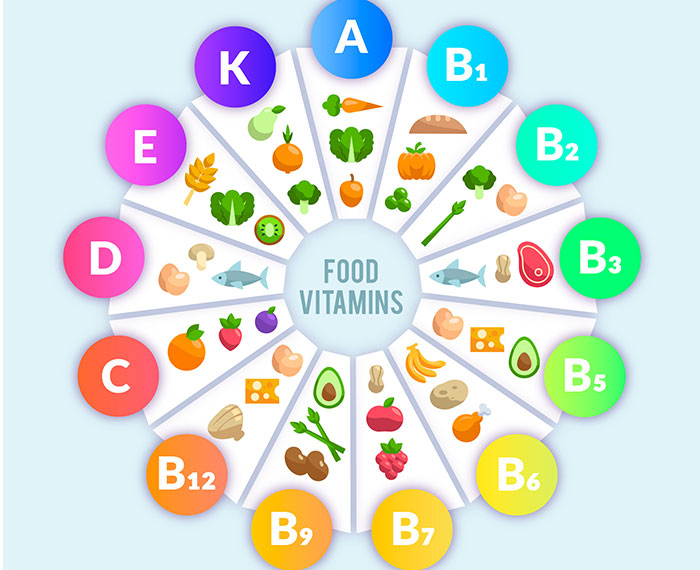
Vitamins A, D, E, C, B1 and B2 are not synthesized in the human body and therefore require external supplementation.
Which foods contain vitamins?
Green vegetables and fruits are full of vitamins. However, their vitamin content has been greatly reduced due to artificial agriculture. Therefore, organic supplementation is required.
What should be considered when using vitamin supplements?
33% of cancer diseases are caused by malnutrition. The diet should be created by determining the need for vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients. In addition, the person’s protein, carbohydrate and calorie requirements should be taken into consideration. Vitamin supplements should be used under the supervision of a physician and nutritionist according to age, gender and needs.
Antioxidants
Free radicals are oxygen molecules that are missing an electron and are considered to be the root cause of many diseases, ranging from cell damage to aging and cancer. Antioxidants are molecules capable of stopping oxidation. They remove free radicals. They react with free radicals and terminate chain reactions. They reduce the risk of abnormalization of cells and consequently tumor formation. Since they also reduce cell destruction, they increase the chances of living a healthier life with minimal effects of aging. Synthetic antioxidants have possible carcinogenic effects. Care should be taken to use natural antioxidants instead of synthetic antioxidants. Low levels of antioxidants or inhibition of antioxidant enzymes can cause oxidative stress and damage cells or lead to their death.
What is the most powerful antioxidant?
Glutathione is the most powerful antioxidant. Vitamins E and C are also powerful antioxidants.
What are natural antioxidants?
Artichokes, walnuts, blueberries, spinach, strawberries, strawberries, beets, raspberries, broccoli, beans and noni berries, which are not available in Turkey, are natural antioxidants.
Antioxidant vitamins
When free radicals increase, the protection of our physical system is overloaded. The organism needs to be supported by antioxidative microbiologists. Folate, vitamins B6 and B12, is essential for homocysteine metabolism and is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease. Inadequate folate intake is associated with neural tube defects and some cancers. Vitamin E and lycopene may reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Zinc, betacarotene and vitamin E reduce the progression of macular degeneration.
What do vitamins do?
- Vitamin A It is an antioxidant. It is involved in building and protecting the skin. Helps to heal wounds. Useful for the eyes
- Vitamin B Composed of 8 different water-soluble vitamins. It cannot be stored in the body, excess is removed from the body.
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine): Provides the energy needed by cells and helps some functions of the nervous system. It plays an active role in the growth and functioning of cells.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin): Helps the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates taken into the body and contributes to the process of producing the energy required for the body. It is involved in the working mechanism of many enzymes in the body.
- Vitamin B3 (niacin): Contributes to the production of energy and the healthy functioning of many enzymes and hormones. It is also involved in the healthy functioning of the digestive and nervous system.
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid): It is transported to different parts of the body via red blood cells and contributes to the process of food-based energy production.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine): It is involved in many areas such as the hormonal system, nervous system, immune system and blood production. It also contributes to the production of red blood cells.
- Vitamin B7 (biotin): Also called vitamin H. It is involved in many metabolic processes such as protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Contributes to cell growth, Dna and protein synthesis.
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid): An absolutely essential vitamin for the production of DNA and RNA. It is necessary for the production of red blood cells and is involved in the conversion of food into energy.
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin): It is a vitamin needed by almost every cell in the body. It is essential for the nervous system, brain function and the production of red blood cells.
- Vitamin C (vitamin C): It is an antioxidant. Supports iron absorption. It contributes to the development of connective tissue and is also important for bones.
- Vitamin D: Provides calcium and phosphate in the bones.
- Vitamin E: It is an antioxidant. It is protective for cells. It supports the healthy functioning of muscles and nerves.
- Vitamin K: It is involved in blood clotting and bone metabolism. It is necessary for the production of a protein called prothrombin.
What do minerals do?
- Copper: It contributes to a healthy metabolism and proper functioning of the nervous system. It also plays a role in keeping bones strong.
- Boron: Plays a role in strengthening bones and muscles.
- Zinc: It is an antioxidant. Supports the healing of wounds.
- Iron: Helps to make red blood cells that carry oxygen to the body. Contributes to strengthening the immune system and cell division.
- Fluorine: Fights tooth decay and contributes to the prevention of osteoporosis.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium to build strong and healthy bones. It plays a role in the repair of tissues and cells.
- Iodine: It has many important functions, especially in energy metabolism. It plays a role in the development of the skeleton and central nervous system of the fetus.
- Calcium: It is of great importance in bone development and maintenance of bone health.
- Chlorine: Helps regulate the amount of fluid in the body and regulates acid-base balance.
- Magnesium: Plays a role in many metabolic processes such as energy production, regulation of blood pressure and nerve signal transmission.
- Manganese: It is effective in the formation of body connective tissue, bone and sex hormones. It is effective in the regulation of blood sugar and growth and development.
- Potassium: Helps body systems to function properly, including heart, muscle and bone health.
- Selenium: Antioxidant. Provides glutathione.
- Sodium: It plays a role in the distribution of water in the body and helps maintain acid-base balance. It also contributes to the transmission of nerve impulses.
Nutritional support for beauty
Free radicals are formed in every process that energizes our body. But our body can scavenge them within certain limits. Almost 80-90% of free radicals come from food. We need to eat enough to make ATP, but little enough to prevent free radicals from forming too much.
Fats
Fats should make up 20-30% of your daily calorie intake. This amount consists of 3 parts. These are saturated fats, monounsaturated fats (omega-9) and polyunsaturated fats (omega-3 and omega-9). Unsaturated fats provide stability in our cells and ensure efficient blood and oxygen utilization. They are essential for our immune system.
What does omega-3 do?
Omega-3 fatty acids are fatty acids that cannot be produced in our body and we need to get from outside with food. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in the cell membrane. They protect cells during physical activity. It has a positive effect on blood. When used regularly, it lowers LDL cholesterol and helps increase HDL cholesterol. Regulates blood pressure while lowering triglycerides. Reduces the risk of heart attack. Slows down the formation of arteriosclerosis despite high intake of fatty and protein foods. Excessive intake of saturated fat or animal fat increases the risk of colon and breast cancer. The risk of colon carcinogenesis is reduced after a diet with omega-3. Administration of fish oil improves the patient’s condition during cancer cachexia, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. It helps prevent dyslexia, cerebrovascular diseases, dementia, schizophrenia, behavioral disorders, depression, stress, autoimmune diseases and allergic diseases.
Foods containing omega-3
We can get the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) directly from fish. In order to be protected from toxic chemicals and heavy metals, it is necessary to pay attention to the fish oil taken and to prefer purified ones. It has been found that omega-3 levels are much lower in cooked fish.
Uses of Omega-3
- Pregnancy period
- Supporting children’s intellectual development and immune systems
- Heart health
- Bone and joint health
- Skin health
Omega-3 use in pregnancy
Omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy helps to support the development of the baby’s brain, eyes and nervous system, prevent postpartum depression, reduce the risk of premature birth and reduce the risk of allergy and asthma development in the child.
Omega-3 for heart health
The American Heart Association recommends 2-4 grams for lowering triglyceride levels and 1 gram of EPA and DHA per day for individuals with coronary heart disease.
Omega-3 use in children
Supports brain, eye and nervous system development. Increases learning skills, problem solving ability and concentration. Supports the treatment of attention deficit and hyperactivity. Strengthens the immune system. Supports protection against allergic diseases. Reduces the incidence of asthma symptoms.
What is CLA (conjugated linoleic acid)?
It is a free unsaturated fatty acid found naturally in meat and dairy products. To get the benefits of CLA, you need to consume significant amounts of these foods. This is not only impractical but also damages our body with negative effects due to high calories and protein. In particular, a 65% decrease in the amount of CLA contained in livestock has been observed as a result of feeding them with artificial feed instead of feeding them in pastures.
Benefits of CLA
It affects the balance of muscle and fat in the body. It plays a very important role in reducing stored fat and increasing lean muscle. Regular intake of CLA prevents the lipoprotein-lipase enzyme from working and reduces the amount of fat stored in the body, as well as releasing previously stored fat. It has anticatabolic, antioxidant, immune system booster, cholesterol-lowering and anti-cancer effects. CLA can also reduce the risk of breast cancer, prostate cancer and atherosclerosis. It can also help diabetics control their blood sugar.
Magnesium benefits
Helps the healthy functioning of the muscular and nervous system. It is involved in hundreds of enzymatic reactions. 65% of magnesium is found in bones and teeth. Slowing down the aging process with antioxidants can be strengthened with magnesium. Zinc is required for energy-dependent magnesium accumulation in heart mitochondria. Magnesium deficiency prevents the use of vitamin D. Correction of magnesium deficiency corrects vitamin D resistance in children and adults.
What is ORAC?
ORAC (oxygen radical absorbance capacity) is a scale for nutrients that work to destroy free radicals that cause various diseases.
Foods with the highest ORAC value
Gojiberry 34,000
Pomegranate 10,000
Blueberry 4.750
Blackberry 2,650
Strawberry 2,500
Spinach 2,400
Orange 1.475
Onion 875
Red pepper 710
Carrot 275
Tomato 189
Watermelon 104
Nitric oxide
It is a signaling molecule that must be present in our body and has a role in the regulation of physiological and cellular processes in tissues. It allows nutrients to enter the cell. Today’s living conditions, malnutrition, the aging process and stress reduce nitric oxide production. In addition, the body’s production of nitric oxide starts to decrease gradually from the 20s onwards. The trend and speed of this decrease varies from person to person. Even the rate of decrease in different organs in the same person varies. Nitric oxide is important for the occurrence of diseases and for us to recognize them. Not only does the rate of decrease vary from person to person, but the organs affected may also be different depending on the person’s situation, habits and diet.
Vitamin D synthesis
Our bodies need sunlight to produce vitamin D. UV-B rays must come at right angles. In our country, sunlight does not fall at right angles between October and April. In other months, between 11.00-15.00 pm, at least 3 days a week, 35-40% of the body should be exposed to direct sunlight.
What are the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency?
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle pain for no reason
- Chronic fatigue
- Increased risk of fracture