Flu, Colds and Coughs
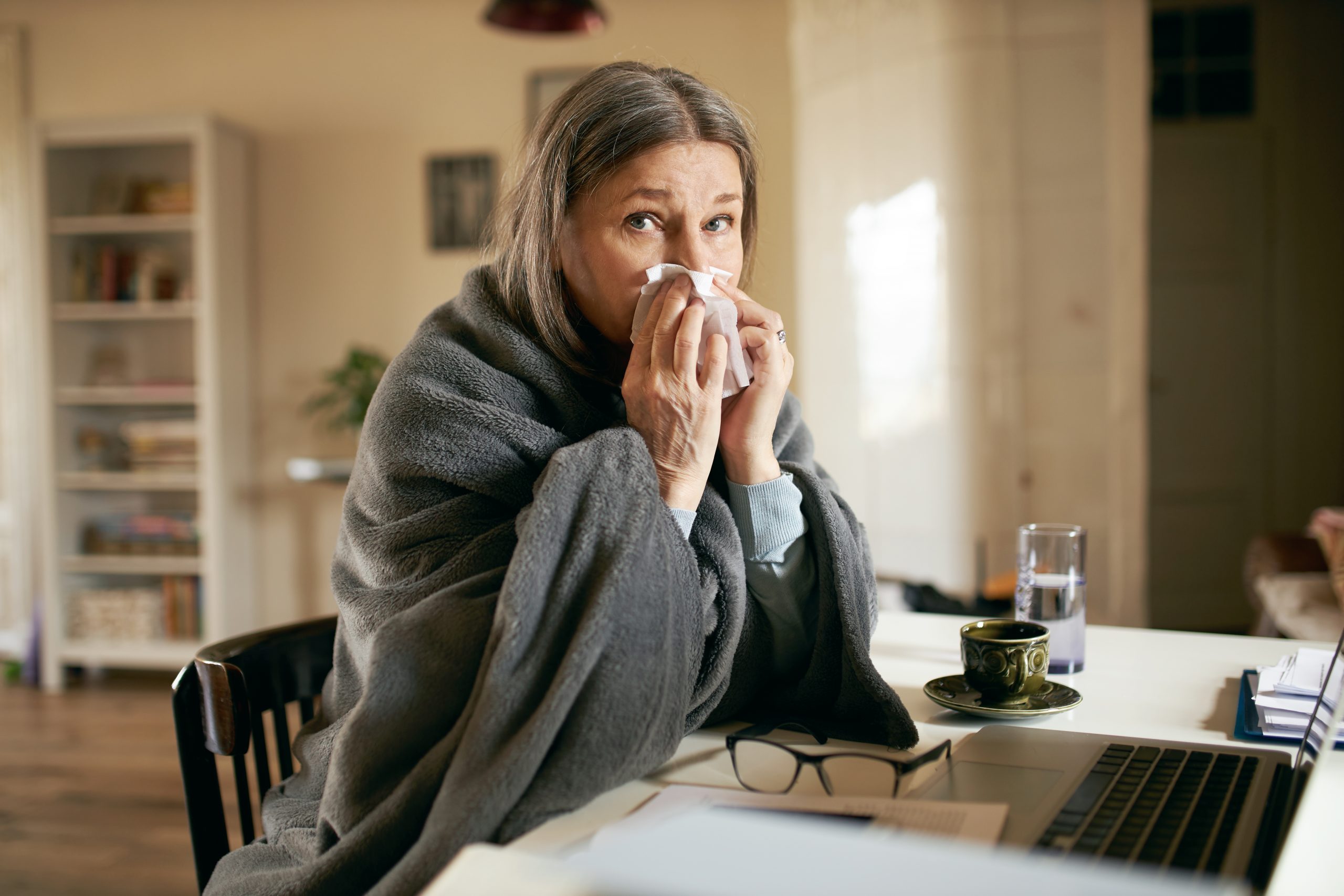
It is important to know the difference between flu and cold symptoms. A cold is a respiratory illness with milder symptoms than the flu. Cold symptoms can make you feel unwell for a few days, while flu symptoms can make you feel quite bad for a few days to a few weeks. Flu can also lead to serious illnesses such as pneumonia if not treated properly.
What are the symptoms of a cold?
Cold symptoms usually start with a sore throat that will disappear after a day or two. A runny and stuffy nose is accompanied by a cough on the fourth and fifth day. A mild fever, although possible, is usually rare in adults, but it is normal for a child to have a fever when they have a cold.
During the first few days of a cold, the nose is full of mucus. Later this watery mucus becomes thicker and darker. Dark snot is natural and does not usually mean that you have developed a bacterial infection, such as a sinus infection. Cold symptoms last for up to a week. It is contagious during the first three days when symptoms are intense. It is therefore important to avoid contact with others and rest at home.
If the symptoms of a cold persist a week after contracting the illness, this may indicate a bacterial infection. You should consult a doctor and take antibiotics as prescribed for the possible risk of infection.
Sometimes allergic rhinitis (hay fever) or sinus infection is confused with the symptoms of a cold. The common cold should get better in a week, if it does not get better, you can consult your doctor to find out if it is caused by allergies or sinusitis.
What are common flu symptoms?
Flu symptoms are usually more severe than those of the common cold and come on quickly. They include runny nose and eyes, sore throat, fever, headache, muscle aches, nasal congestion and cough. If the flu is swine flu, vomiting and diarrhea are also symptoms.
Most flu symptoms gradually improve over two to five days, but you may continue to feel exhausted for a week or more. A common complication of flu is pneumonia, especially in young people, the elderly and people with lung and heart problems. If you notice shortness of breath, tell your doctor. Another common symptom of pneumonia is fever, which occurs every one to two days.
As with cold viruses, flu viruses enter your body through the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes and mouth. You can infect yourself by touching your hand in one of these areas. Proper hand hygiene is the most important step in preventing flu and colds.
Flu or Cold?
How do you know whether your symptoms are flu or cold? First of all, you should take your temperature. Fever is one of the most common symptoms of flu. Flu symptoms are usually similar to those of a cold, with a stuffy nose, dry cough, aches and pains and weakness. However, colds rarely show a fever above 38 degrees Celsius. The flu, probably when you are infected with the influenza virus, raises your temperature and makes you feel unhappy and quite weak. Body and muscle aches and pains are also more common with flu than with colds.
When should I go to the doctor?
It is important to see a doctor if you have any of the following serious symptoms:
Persistent fever: A fever that lasts for more than three days may be a sign of another bacterial infection that needs to be treated.
Painful swallowing: While a sore throat from colds and flu can cause mild discomfort, severe pain may indicate another condition that requires treatment by a doctor.
Persistent cough: When the cough does not go away even after two or three weeks, there is a high likelihood of developing bronchitis and the use of antibiotics is essential to treat bronchitis. Postnasal drip or sinusitis can also cause a persistent cough. In addition, asthma is another cause of a persistent cough.
Persistent nasal congestion and headache: Colds and allergies cause the sinuses to become blocked, which can lead to a sinus infection (sinusitis). If pain around the eyes and a persistent runny nose persist for more than a week, you may have a bacterial infection and need antibiotics. However, most sinus infections do not always need antibiotics.
In some cases, you may need to seek emergency medical help. Symptoms of a crisis in adults include
- Severe chest pain
- Severe headache
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Persistent vomiting
Signs of an emergency in children include
- Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing
- Bluish skin color
- Dry mouth
- Lethargy and failure to communicate normally
- Extreme irritability
- Symptoms that improve and then suddenly worsen
- Skin rash
- Fire
How can I prevent colds and flu?
The most important measure to prevent colds and flu is frequent hand washing. Rubbing hands with warm soapy water for at least 20 seconds helps kill germs on the skin.
In addition to hand washing to prevent flu or cold symptoms, you can also get a flu shot to prevent seasonal flu. Seasonal flu usually lasts from late December to early March. Within two weeks of receiving the flu vaccine, antibodies develop in the body and provide protection against the flu. Children getting the vaccine for the first time need two doses, one month apart.
Another way to protect against flu is antiviral medicine. Antiviral medicines can be used within the first 48 hours of contact with someone who has the flu virus to prevent illness.
Finally, it should be emphasized that antibiotics are only prescribed for bacterial infections. Flu and colds caused by viruses are not treated with antibiotics.